Medical laboratories play a pivotal role in healthcare, providing accurate and reliable diagnostic information that influences medical decisions. To ensure the highest standards of quality, accuracy, and patient safety, medical laboratories can seek accreditation from the NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories). Let’s explore the NABL accreditation process specific to medical laboratories and its significance in the healthcare landscape:
What is NABL Accreditation for Medical Laboratories?
NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories) accreditation for medical laboratories is a formal recognition granted to laboratories that perform medical testing and diagnostics, indicating their compliance with internationally recognized quality and competence standards. This accreditation is a testament to the laboratory’s commitment to maintaining the highest levels of accuracy, precision, and reliability in their testing procedures and practices.
NABL, an autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology of the Government of India, establishes rigorous standards for the operation, management, and performance of medical laboratories. These standards are aligned with international guidelines, including the ISO 15189 standard for medical laboratories. The accreditation process involves a comprehensive assessment of various aspects of the laboratory’s operations, including quality management systems, personnel competence, equipment calibration, testing methodologies, documentation practices, and adherence to ethical standards.
Achieving NABL accreditation for a medical laboratory signifies that the laboratory has successfully met or exceeded the specified quality standards, ensuring that the laboratory’s testing results are accurate, reliable, and consistent. This accreditation is a mark of excellence and signifies that the laboratory has undergone a thorough evaluation by experienced assessors who are experts in the field of medical diagnostics.
NABL accreditation for medical laboratories is highly regarded in the healthcare industry. It instills confidence among healthcare professionals, patients, regulatory authorities, and stakeholders in the accuracy and reliability of the laboratory’s test results. Accredited laboratories are recognized for their commitment to maintaining the highest standards of patient care, quality, and safety.
NABL Accreditation Process: Steps and Overview
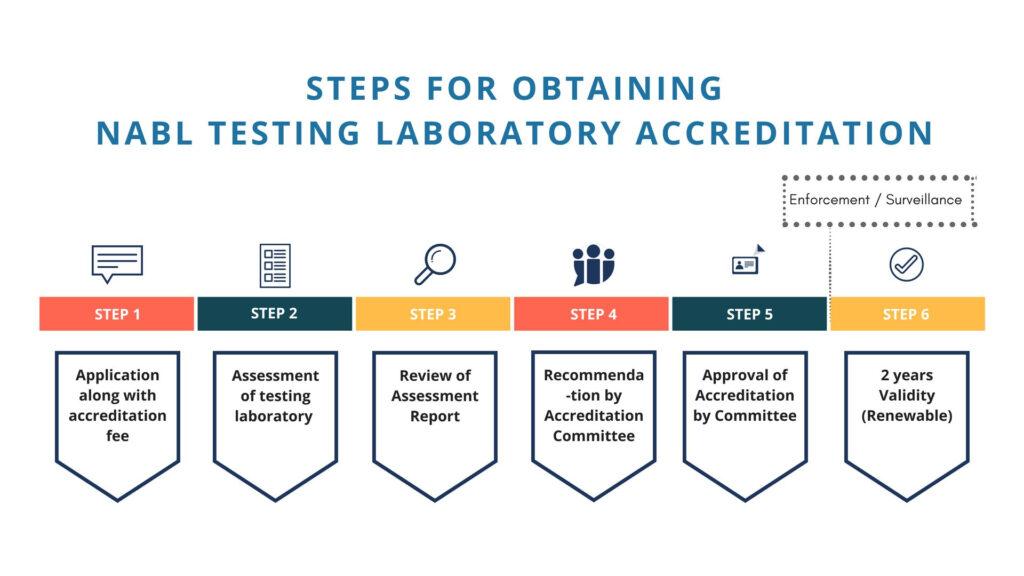
The accreditation process involves several stages to ensure that medical laboratories meet internationally recognized guidelines for accurate and reliable testing. Below is an overview of the steps involved in the NABL accreditation process for medical laboratories:
1. Application:
The process begins when a medical laboratory expresses its interest in seeking NABL accreditation. The laboratory submits an application to NABL, indicating the scope of tests and diagnostics for which accreditation is sought.
2. Document Review:
NABL assessors review the laboratory’s quality management system documentation. This includes policies, procedures, protocols, and other relevant documents. The aim is to ensure that the laboratory’s practices align with the quality standards specified in ISO 15189, the international standard for medical laboratories.
3. Pre-Assessment Visit:
In some cases, NABL may conduct a pre-assessment visit. During this visit, NABL assessors provide the laboratory with insights into the accreditation process and identify areas that may require improvement. This step helps the laboratory prepare for the formal assessment.
4. Formal Assessment:
The formal assessment is a comprehensive evaluation of the medical laboratory’s operations. NABL assessors visit the laboratory to assess its facilities, equipment, personnel competence, testing methodologies, documentation practices, and adherence to quality protocols. The assessment involves interviews, observations, and reviews of records.
5. Assessment Report:
Based on the formal assessment, NABL generates an assessment report. This report outlines the laboratory’s strengths, areas for improvement, and any non-conformities—instances where the laboratory’s practices do not align with accreditation standards.
6. Corrective Actions:
If non-conformities are identified, the medical laboratory addresses them by implementing corrective actions. These actions aim to rectify the issues and bring the laboratory’s practices in line with the required standards.
7. Final Assessment:
NABL assessors conduct a final assessment to ensure that the corrective actions have been successfully implemented. This assessment confirms that the laboratory’s operations now meet the required standards.
8. Accreditation Decision:
Based on the assessment process, corrective actions, and adherence to standards, NABL makes an accreditation decision. If the medical laboratory meets the necessary requirements, it is granted NABL accreditation.
9. Ongoing Surveillance:
NABL-accredited medical laboratories are subject to regular surveillance visits. These visits are conducted to ensure that the laboratory continues to maintain the accredited level of quality in its operations.
Benefits of NABL Accreditation for Medical Laboratories
Accreditation by the NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories) is a significant achievement for medical laboratories. It reflects a commitment to quality, accuracy, and patient safety. NABL accreditation offers a range of benefits that contribute to the enhancement of medical laboratory services and the overall healthcare landscape:
1. Enhanced Patient Safety and Care:
NABL accreditation ensures that medical laboratories adhere to stringent quality standards. Accurate and reliable test results are crucial for proper patient diagnosis and treatment. Accredited laboratories provide healthcare professionals with trustworthy information, contributing to improved patient care and safety.
2. Credibility and Trust:
NABL accreditation signifies that a medical laboratory has been rigorously assessed and found to meet or exceed internationally recognized standards. This achievement enhances the credibility and trustworthiness of the laboratory’s test results among healthcare professionals, patients, and stakeholders.
3. Global Recognition:
NABL-accredited medical laboratories are recognized not only within India but also on the international stage. This recognition can open doors to collaborations, partnerships, and opportunities to contribute to global healthcare initiatives.
4. Continuous Improvement:
The accreditation process encourages medical laboratories to adopt a culture of continuous improvement. Laboratories are motivated to review and refine their processes, enhancing the quality and accuracy of their services over time.
5. Efficiency and Effectiveness:
Accreditation prompts medical laboratories to streamline their operations, improve workflows, and optimize resource utilization. This leads to increased efficiency, reducing the risk of errors and delays.
6. Staff Competence and Training:
NABL accreditation places emphasis on the competence and training of laboratory personnel. Staff members are required to demonstrate their skills and knowledge, ensuring that the laboratory team is well-equipped to perform accurate and reliable tests.
7. Adherence to Best Practices:
Accredited medical laboratories are committed to following internationally recognized best practices in testing, quality management, and safety. This commitment translates into high-quality services and consistent results.
8. Quality Management:
NABL accreditation necessitates the implementation of robust quality management systems. This ensures that every aspect of the laboratory’s operations is monitored, evaluated, and continually improved to meet the highest standards.
9. Compliance with Regulations:
Accreditation helps medical laboratories align with regulatory requirements and guidelines. This is particularly important in a healthcare landscape where adherence to standards is paramount for patient safety and legal compliance.
10. Stakeholder Confidence:
Stakeholders, including patients, clinicians, healthcare organizations, and regulatory bodies, have confidence in the services provided by NABL-accredited medical laboratories. This confidence is rooted in the knowledge that the laboratory’s operations are transparent, consistent, and of the highest quality.
Conclusion
The NABL accreditation process for medical laboratories is a journey toward excellence in testing and diagnostics. Achieving accreditation signifies the laboratory’s commitment to providing accurate and reliable results while adhering to internationally recognized quality standards. The process not only enhances the laboratory’s reputation but also contributes to the overall improvement of healthcare services by ensuring the delivery of accurate and reliable diagnostic information.
Medical laboratories seeking NABL accreditation should embrace the process as an opportunity for continuous improvement and the advancement of patient care and safety.
References
- NABL Official Website:
- National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL). https://www.nabl-india.org/
- ISO 15189:
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 15189:2012 – Medical laboratories – Requirements for quality and competence. https://www.iso.org/standard/56115.html
- NABL Accreditation Process Overview:
- NABL Accreditation Process for Medical Laboratories. https://nabl-india.org/accreditation-process/
- Quality Management in Medical Laboratories:
- Zima T. Accreditation of Medical Laboratories – System, Process, Benefits for Labs. J Med Biochem. 2017 Jul 14;36(3):231-237. doi: 10.1515/jomb-2017-0025. PMID: 30568539; PMCID: PMC6287213.
- Patient Safety and NABL Accreditation:
- Adhikari, P. (2017). Importance of Accreditation in Quality Improvement of Medical Laboratories. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences, 8(3), 76-82.
- Healthcare Quality Improvement:
- Kalaiselvan, G., Srinivasan, R., Gopinath, G., & Manickam, P. (2014). Quality Management in Health Care. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 8(6), IE01-IE03.
- Laboratory Accreditation Impact on Patient Outcomes:
- Ismail, A. M., Osman, R. A., & Farag, A. B. (2018). The Impact of Laboratory Accreditation on Patient Care and the Healthcare System. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, 19(4), 315-321.
